Title: 4,000-Year-Old Mysterious Rock Unveils Ancient ‘Treasure Map’ in France
Introduction:
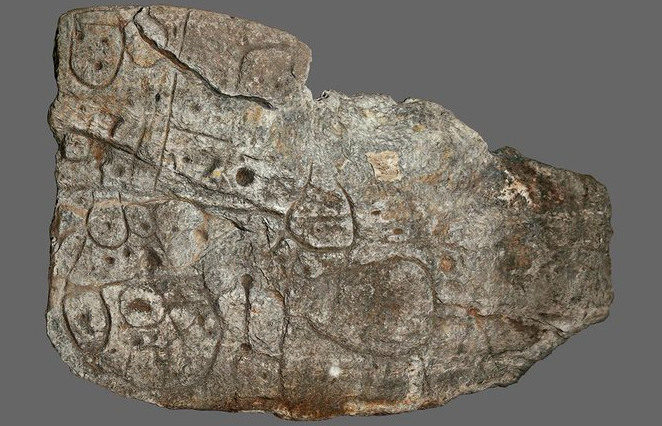
In a groundbreaking discovery, an ancient slab of granite with mysterious symbols has captivated archaeologists in northwest France. Known as the Saint-Belec slab, this enigmatic artifact has recently been hailed as a “treasure map” that holds the key to uncovering long-lost ancient locations. With its potential as a valuable archaeological tool, researchers are now deciphering its engravings to precisely date the slab and shed light on ancient structures.
The Importance of the Saint-Belec Slab:
Discovered in 1900 by Paul du Châtellier in Finistère, the Saint-Belec slab has gained recognition as Europe’s earliest known map. Situated next to a grave, its markings have sparked the curiosity of scholars. Archaeologists are now utilizing the map to identify and explore archaeological sites, a novel approach in the field. Previously, ancient sites were usually unearthed accidentally during urban development or through advanced technologies like radar or aerial photography.
Unlocking the Mystery:
Covering an area of approximately 30 by 21 kilometers, the Saint-Belec slab encompasses the Brittany region of Roudouallec, which is about 500 kilometers west of Paris. Researchers have discovered that about 80% of the map corresponds to the present geographic data, indicating its accuracy. However, the meaning behind the geometric symbols and their associated stories remains unknown. The tiny hollows on the slab have led experts to speculate that they could represent various elements such as homes, housing mounds, or geological deposits. Further investigation into these mysterious patterns may unveil a wealth of new findings.
A Glimpse into Bronze Age Society:
Excavations near the location where the Saint-Belec slab was initially found have shed light on it being one of the most significant Bronze Age burial sites in Brittany. Recent discoveries of previously unknown fragments of the slab indicate that it was shattered and repurposed to construct a tomb wall. This suggests a shift in power dynamics within the Bronze Age settlement. The map on the slab may depict an ancient kingdom that experienced uprisings and other forms of unrest, providing valuable insights into the societal structures of the time.
Interpreting the Saint-Belec Slab:
Researchers have compared the Saint-Belec slab to depictions found among different ethnic groups and prehistoric Europe. Its repetitive motifs connected by lines suggest a geographical arrangement. According to experts, the slab represents the domain of a hierarchical governing body that exerted tight authority over the region during the early Bronze Age. The presence of broken slabs may indicate the censure and deconsecration of early Bronze Age elites, marking the end or rejection of long-standing rulers.
Conclusion:
The discovery of the 4,000-year-old Saint-Belec slab in France has brought excitement to the world of archaeology. This ancient “treasure map” offers a unique opportunity to retrace the steps of our ancestors and gain a deeper understanding of their societies. Although there is still much to be unravelled, the slab holds the promise of uncovering hidden archaeological sites and rewriting our understanding of the past. As researchers delve deeper into the enigmatic symbols and patterns engraved on the slab, the secrets of the ancient world are slowly being unveiled.

I have over 10 years of experience in the cryptocurrency industry and I have been on the list of the top authors on LinkedIn for the past 5 years. I have a wealth of knowledge to share with my readers, and my goal is to help them navigate the ever-changing world of cryptocurrencies.