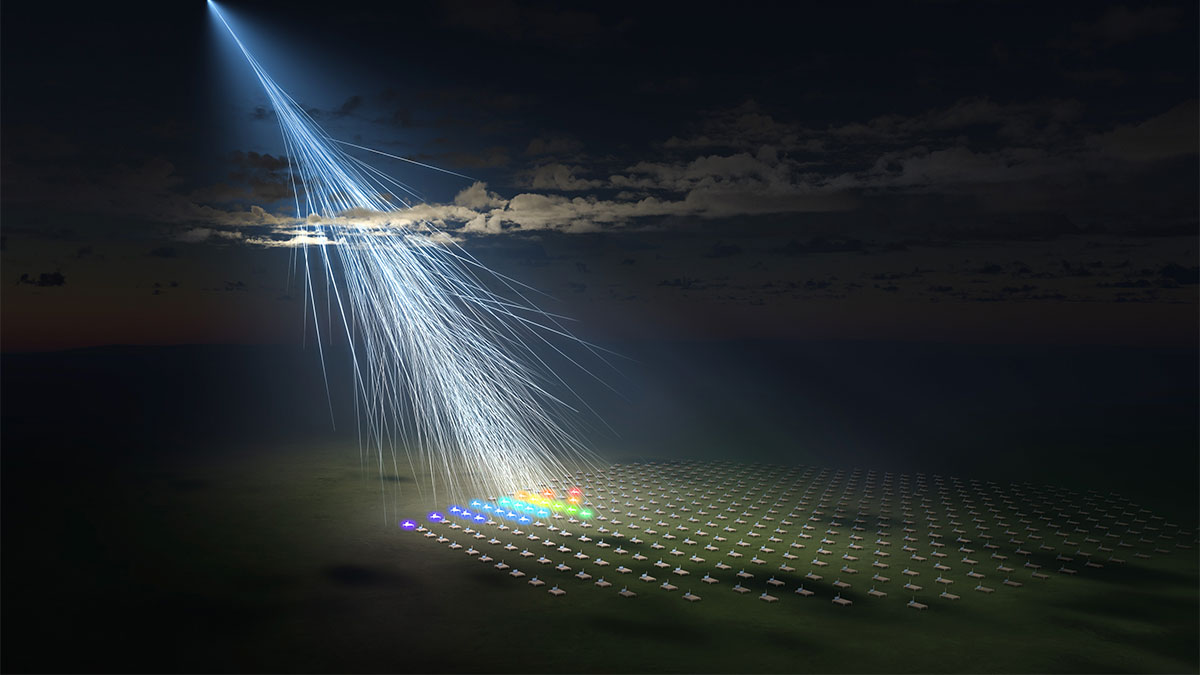
The Telescope Array, comprising 507 surface detector stations covering an expansive 700 km², detected the second-highest extreme-energy cosmic ray ever observed on May 27, 2021. The remarkable discovery, led by the University of Utah and the University of Tokyo, demonstrated an energy level of 2.4 x 10^20 electron volts (eV). The incident activated 23 detectors in the northwest sector of the array, indicating that the particle’s path seemed to initiate from the Local Void, a vacant expanse in space adjacent to the Milky Way galaxy.
Both the Oh-My-God and Amaterasu particles significantly surpassed the theoretical boundary called the Greisen-Zatsepin-Kuzmin (GZK) cutoff, raising questions about particle physics yet unknown to science. The researchers noted that the composition of the particle is likely a proton, introducing an additional element of mystery. Astrophysicists have detected over 30 ultra-high-energy cosmic rays, but none approaching the Oh-My-God-level energy, and their origin and how they can travel to the Earth remain under investigation.
Telescope Array co-author John Belz suggests unconventional possibilities and said, “It could be defects in the structure of spacetime, colliding cosmic strings.” The array aims to capture more cosmic events and shed light on the perplexing nature of these ultra-high-energy cosmic rays, with the team’s findings published in the journal Science. The Telescope Array’s unique setup, with detectors covering a vast area, allows researchers to study the trajectory and energy of these cosmic rays.
The cosmically groundbreaking discovery is reminiscent of the famed Oh-My-God particle detected by the University of Utah Fly’s Eye experiment in 1991, marking a significant milestone in astrophysics. This ultra-high-energy cosmic ray, dubbed the Amaterasu particle, is the second-highest ever observed and raises questions about particle physics yet unknown to science. As astrophysicists grapple with this cosmic mystery, the expanded Telescope Array aims to unravel the secrets hidden within these extraordinary particles.
The Telescope Array experiment signifies a significant leap in astrophysics, with the potential to unlock groundbreaking revelations about cosmic rays and the universe. This single subatomic particle is equivalent to dropping a brick on your toe from waist height, reflecting its extraordinary energy levels. John Matthews, a co-spokesperson of the Telescope Array experiment, explained the puzzle surrounding these high-energy particles by saying, “The particles are so high energy, they shouldn’t be affected by galactic and extra-galactic magnetic fields.” Researchers have named this ultra-high-energy cosmic ray the Amaterasu particle, drawing inspiration from the sun goddess of Japanese mythology.
The study, published in the journal Science, marks a significant leap in astrophysics research and could shape future understanding of cosmic rays and the universe. The revelations from the Telescope Array experiment offer a new frontier for scientific inquiry, sparking renewed curiosity about the origins and behavior of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays.